Embedded Linux Conference 2013
San Francisco, CA Feb 20-22, 2013
Advanced Filters
Unlock powerful filtering options to find exactly what you're looking for with our premium subscription.
Conference Videos
33 results

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Flash Friendly File System
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Flash Friendly File System (F2FS) By Joo-Young Hwang San Francisco, California Recent mobile devices adopt various flash storages as a primary storage. File system support for those flash storages is a must for flash device performance and lifespan.I will present a new file system, called F2FS, designed for mobile flash storages. F2FS is designed considering the characteristics of the underlying flash storage which has flash translation layer (FTL). F2FS outperforms EXT4, which is a popular file system for Android phones, in most of benchmarks. I will describe motivation, design, and implementation of the file system, then show performance comparison data with EXT4. Target audiences are those who are interested in file system support for flash storages such as eMMC and SSD. Kernel and file system expertise helps but is not mandatory to listen to this talk.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Pin Control and GPIO Update
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Pin Control and GPIO Update By Linus Walleij San Francisco, California This session is intended to sum up the last say 24 months of changes with the creation of the pin control system and the changes related to GPIO as well as changes to the GPIO subsystem per se. We will know about the systems migrated to pin control, how device tree is used, pin to GPIO range mappings from either end, block GPIO control and how we try to move forward.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - The Embedded Linux Problem
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 The Embedded Linux Problem By Mark Gross San Francisco, California Intel's reference BSP / Android stack for its last 3 generations of SOC has been experiencing the challenges of the "embedded problem" where we get a hardened kernel / OS stack hardened on time scales larger than the Linux release cycle. This results in harder efforts WRT upstreaming drivers and a failure to enable any community participation for SOC specific driver work. This talk will introduce the scope of the effort WRT the intel SOC's and explain how we've fell into the problem. Then we will go into how we are trying to address the problem more effectively.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Task Scheduling for Multicore Embedded Devices
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Task Scheduling for Multicore Embedded Devices By Gap-Joo Na San Francisco, California Gap-Joo Na received the MS and PhD degrees in computer engineering from Sungkyunkwan University, Korea, in 2006 and 2011. Currently he is a senior researcher at Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Korea. His research area is embedded software platforms using Linux and his research interest include flash-based database technology and flash file system.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Flattened Image Trees: A Powerful Kernel uImage Format
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Flattened Image Trees: A Powerful Kernel uImage Format By Joel A. Fernandes San Francisco, California The legacy U-boot image format is quickly becoming outdated as multi-component images are quickly becoming necessary. Images now not only carry a kernel, but also a device tree blob, ramdisk image etc for instance. With the increasing importance of security, storing multiple signatures and certificates structures in an image are also becoming common. The struct image_header in the legacy U-boot image format is not flexible enough to cover all multi image formats. Components of a kernel boot image might have to be loaded into different parts of memory before booting. A new image format (Flattened Image tree) similar to FDT solves some these problems. Audience is U-boot and Kernel developers who work on kernel boot and security boot. They can expect an introduction to FIT, its motivation, advantages with an example. Technical Expertise required is familiarity with kernel boot mechanisms.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Inside the RT Patch
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Inside the RT Patch By Steven Rostedt San Francisco, California The real-time patch (which provides CONFIG_PREEMPT_RT), has been around since 2005. Started by Ingo Molnar and maintained by Thomas Gleixner and several others, it has grown from a hobby RTOS into a very serious contender. Several distributions (Red Hat, SuSE, Debian, Ubuntu) supply a kernel version that includes this patch. The embedded world has started adding the -rt patch to their own devices that they ship. But do the embedded developers understand what the -rt patch supplies? Programming for real time, and especially when writing kernel code requires special knowledge to avoid real time traps. This talk will explain what the real time patch provides and special programming tips that will ensure embedded developers will get the best from their devices.
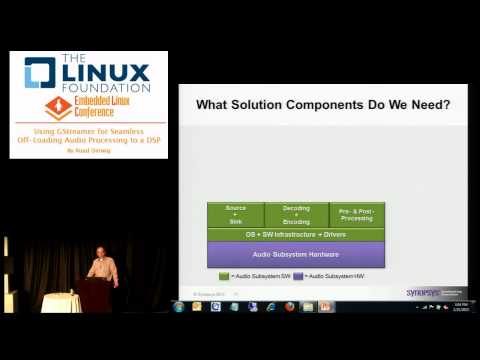
Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Using GStreamer for Seamless Off-loading Audio Processing
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Using GStreamer for Seamless Off-loading Audio Processing to a DSP By Ruud Derwig San Francisco, California This session explains how off-loading audio processing from an application CPU to an audio DSP is made easy using GStreamer. Despite the compute power of multicore application CPUs, the SoC design trend is heterogeneous with specialized subsystems and cores. For power efficiency and hardware cost such SoCs are optimal, for developers they are a pain. In the homogenous case SMP-Linux hides complexities, in the heterogeneous case developers must deal with different tools, shared memory (coherency), multiple OSes, optimization of DSP code, etc. Solutions as remoteproc are a first step in simplifying the use of the different cores on a SoC. We take this basic management and control a step further by leveraging the domain specifics of audio processing. The complexities of off-loading are hidden inside GStreamer elements, while retaining the flexible, plug-and-play graph creation of GStreamer.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Toybox: Writing a New Command Line From Scratch
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Toybox: Writing a New Command Line From Scratch By Rob Landley San Francisco, California This panel explains what's in the "standard" Linux command line: drawing commands from POSIX, LSB, Android Toolbox, Linux From Scratch, and more. How to determine what should be in the base system, and how to know what to exclude, and why the "standards" aren't enough.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - External Pre-built Binary Toolchains
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 External Pre-built Binary Toolchains in Yocto Project By Denys Dmytriyenko San Francisco, California Talk about existing available support for using external pre-built binary toolchains in the Yocto Project. What is provided and how to use it. What are the limitations - uncover and explain ways of overcoming those. Overview examples of existing implementations for using toolchains from CodeSourcery and Linaro, as well as adding support for new toolchains, such as from the Arago Project. Provide the guideline for rolling own pre-built binary toolchain from the Yocto Project and tips for making it usable inside of the Yocto for building filesystem images and SDKs. As well as what's missing and how to enable re-packaging it in the resulting SDK, that can be fed back into the Yocto Project again, completing the circle. Delve into Canadian-cross, associated pros and cons - benefits of self-contained binaries, "relocatability" issues and mixing canadian with regular cross binaries.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Target Communications Framework
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Target Communications Framework: One Link to Rule Them All By Anna Dushistova San Francisco, California The Target Communication Framework (TCF) is a vendor-neutral, lightweight, extensible network protocol for communicating with embedded systems. TCF is designed to transparently plug in value-adding servers between the tool and the target. But even without the value adds, the protocol has the potential to unify many currently independent communication links, thus saving resources and making setup and configuration much easier than in current embedded development scenarios. In this talk we will give an overview of the TCF architecture and provide examples that demonstrate its potential for facilitating development. The presentation is aimed at embedded Linux developers as well as remote tools integrators.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - olibc: Another C Runtime Library
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 olibc: Another C Runtime Library for Embedded Linux By Jim Huang San Francisco, California olibc is derived from bionic libc used in Android, which was initially derived from NetBSD libc. olibc is expected to merge the enhancements done by several SoC vendors and partners, such as Qualcomm, TI, Linaro, etc., which is known to be the major difference from glibc, uclibc, and other traditional C library implementations. Typically, the code size of olibc runtime should be about 300 KB. For ARM target, olibc would benefit from ARMv7 specific features like NEON, Thumb-2, VFPv3/VFPv4, and latest compiler optimization techniques. Also, olibc is released under BSD License.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Namespaces for Security
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Namespaces for Security By Jake Edge San Francisco, California Namespace support has been growing in the Linux kernel, so there are now a number of ways that namespaces can be used to help protect Linux systems (embedded or otherwise) from exploits. Using namespaces (in particular, the mount, network, and user namespaces) can isolate processes in ways that will prevent some types of vulnerabilities from compromising more of the system. Namespaces can be used as part of a "defense in depth" strategy to avoid the harm (or most of the harm) from exploits of vulnerable user-space applications. This talk will be for developers of embedded systems, particularly "system level" developers. It will assume some knowledge of C and Linux, but not require in-depth knowledge of either. Participants can expect to come away with a good foundation on what namespaces are and can do, along with concrete ideas of how to use namespaces in their projects.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Listening to your Users: Refactoring the Yocto Project
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Listening to your Users: Refactoring the Yocto Project By Elizabeth Flanagan San Francisco, California The yocto-autobuilder has been a critical part of the yocto projects ability to deliver predictable releases. However the ability for others to leverage this success has been difficult at times. This talk will introduce the new yocto-autobuilder architecture, the reasons behind the effort and introduce the new features (mix and match layer support, custom build steps, custom properties) and the projects plans for implementation.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - In Kernel Switcher: A Solution
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 In Kernel Switcher: A Solution to Support ARM's New big.LITTLE Implementation By Matheiu Poirer San Francisco, California The 'In Kernel Switcher' (IKS) is a solution developed by Linaro and ARM to support ARMâs new big.LITTLE implementation. It is pairing together an A7 (LITTLE) and an A15 (big) processor into a logical entity that is then presented to the kernel as one CPU. From there the solution is seeking to achieve optimal performance and power consumption by switching between the big or the LITTLE core based on system usage. This session will present the IKS solution. After giving an overview of the big.LITTLE processor we will present the solution itself, how frequencies are masqueraded to the cpufreq core, the steps involved in doing a âswitchâ between cores and some of the optimisation made to the interactive governor. The session will conclude by presenting the results that we obtained as well as a brief overview of Linaro's upstreaming plan.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Extending the SWSUSP Hibernation Framework to ARM
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Extending the SWSUSP Hibernation Framework to ARM By Russell Dill San Francisco, California This talk looks at bringing hibernation support to ARM, with a focus on OMAP. The presentation will include a brief technical overview of the swsusp framework (the mainline hibernation framework), followed by an in-depth discussion of implementations on AM33XX and OMAP3. The talk will also touch on topics closely related to hibernation such as snapshot boot, hibernation restore from bootloader, and self-refresh only suspend/off modes. The presentation is aimed towards embedded developers and hobbyists with an interest in power management. Attendees will gain a greater understanding of swsusp and the technical issues involved in extending support to a new SoC.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - ELC 2013 Security: Best Practices for Embedded Systems
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 ELC 2013 Security: Best Practices for Embedded Systems By John Mehaffey San Francisco, California Computer security concepts are well known, there are many known exploits and ways to counter them, but most of the focus has been on IT systems (servers). Computer security in consumer products is often left to the last minute, if it is implemented at all. In today's increasingly connected world, embedded systems can provide high value targets for hackers, criminal enterprises, and terrorists. Security for embedded computer systems can no longer be left to chance. This talk starts with an overview of security concepts and terms, describes security modules available for Linux, provides some example exploits to provide context, and establishes best practices to ensure that security is built into your product from the start. The talk is appropriate for developers and managers interested in security, but no security experience is assumed.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Easy UI and Elev8
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Easy UI and Elev8 By Leandro Pereira San Francisco, California The Enlightenment Foundation Libraries, although efficient, provides only the most basic building blocks. They also expose a lot of their inner details, which the application programmer must know to use them efficiently. EasyUI is an abstraction layer (written in JavaScript) that helps the programmer by implementing the difficult user interface bits, leaving out the data and behaviour to the programmer. This talk will show what EasyUI is about, with example code and a demo. EasyUI is focused towards usage in mobile devices such as tablets and phones, and will be part of the Tizen SDK.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Bringing kconfig to EGLIBC
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Bringing kconfig to EGLIBC By Khem Raj San Francisco, California Eglibc has had configurability for quite a while now, however lately there has been patches sent for it to use kernel's kconfig infrastructure for managing the configurations This talk will introduce the users and developers to eglibc configurability and how kconfig can be used to achieve that. It will also dive into the various config options currently available and how to use them. Finally it will compare the size footprints with other embedded C library and demonstrate that the size gap can be bridged. It will also demonstrate a distribution poky-tiny which is already taking advantage of configurability

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - An Insight into the Advanced XIP Filesystem (AXFS)
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 An Insight into the Advanced XIP Filesystem By Aaditya Kumar San Francisco, California AXFS is a read only file system which supports both compressed and execute-in-place features. The main advantage of AXFS is that it allows individual pages in an executable image to be XIP or not (as opposed to other XIP systems which require the entire image to be XIP). This results is smaller memory sizes and faster program launches, in some scenarios. However, to achieve this, a profiling pass is required to determine the pages to map directly from the filesystem. Details of the design of AXFS and how to use it will be presented. A performance comparison of AXFS in different usage scenarios will also be shown, including use of AXFS in combination with other optimization techniques. AXFS was recently submitted for inclusion in the LTSI 3.4 kernel release.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Adventures in (Simulated) Asymmetric Scheduling
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Adventures in (Simulated) Asymmetric Scheduling By Pantelis Antoniou San Francisco, California Asymmetric processing, spearheaded by ARM's big.LITTLE architecture, has been touted as a method for solving both the power & performance problem of mobile devices. This architecture requires changes to core scheduling concepts, which are extremely difficult to debug and diagnose, especially since existing tools do not capture useful data for evaluating such a system. A brief overview of the proposed scheduling changes will be presented, with major focus on Paul Turner's load average patches. Methods of simulating an asymmetric system will be described. Additionally a portable process workload capturing method, based on perf, will be presented, i.e. one can capture traces from an Android based system and run it on a standard Linux box. The audience will comprise of kernel scheduler hackers, mobile device developers, and anyone interested in the challenges such a paradigm shift brings.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - KEYNOTE Panel: Is Android The New Embedded Linux
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Android Builders Summit 2013 KEYNOTE Panel: Is Android The New Embedded Linux Mike Anderson, "The PTR group"; Zach Pfeffer, "Linaro"; Tim Bird, "Sony Network Entertainment"; David Stewart, "Intel"; Karim Yaghmour, "Opersys" (Moderator) For a summary of this discussion and more information on defining embedded Linux vs. Android see our recent article on Linux.com: https://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/707796-defining-android-vs-embedded-linux

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - KEYNOTE: Working Together to Accelerate Linux Development
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 KEYNOTE: Working Together to Accelerate Linux Development By Jim Zemlin & George Grey San Francisco, California

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Using and Understanding the Real-Time Cyclictest Benchmark
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Using and Understanding the Real-Time Cyclictest Benchmark By Frank Rowand San Francisco, California

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Optimizing GStreamer Video Plugins
Sep 2, 2025
The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Optimizing GStreamer Video Plugins: A Case Study with Remesas SoC Platform By Katsuya Matsubara San Francisco, California

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - LLVMLinux: Compiling the Linux Kernel with LLVM
Sep 2, 2025
February 21, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 LLVMLinux: Compiling the Linux Kernel with LLVM By Behan Webster

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - How to Decide the Linux Kernel Version
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 How to Decide the Linux Kernel Version for the Embedded Projects to Keep Maintain Long Term By Tsugikazu Shibata

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Building a Custom Embedded Linux Distribution
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Building a Custom Embedded Linux Distribution with the Yocto Project By Sean Hudson

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Common Clock Framework: How to use it
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Common Clock Framework: How to use it By Gregory Clement The common clock framework, which was included in the 3.4 kernel in the beginning of 2012, is now mandatory to support all new ARM SoCs. It is also part of the "one zImage to run them all" big plan of the ARM architecture in the Linux kernel. After an introduction on why we needed this framework and on the problems it solves, we will go through the implementation details of this framework. Then, with real examples, we will focus on how to use this framework to add clock support to a new ARM SoC. We will also show how the device tree is used in this process. The last part of the talk will review how device drivers use this framework, using examples taken from various parts of the kernel.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - KEYNOTE Code Sweat: Embed with Nightmares
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 KEYNOTE Code sweat: Embed with Nightmares By Dave Stewart

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Can you Market an Open Source Project?
Sep 2, 2025
February 21, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Can you Market an Open Source Project? By Tracey Erway and Nithya Ruff

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Controlling Multi-Core Race Conditions on Linux/Android
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Controlling Multi-Core Race Conditions on Linux/Android By Mike Anderson Multi-core processors are now the rule rather than the exception in high-end applications. But, as we try to port our legacy applications to multi-core platforms, what pitfalls lay in wait? This presentation will outline the conditions that lead to multi-core race conditions and outline the techniques for identifying and redesigning code to successfully function in a multi-core world.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Atom for Embedded Linux Hackers and the DIY Community
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Atom for Embedded Linux Hackers and the DIY Community By Scott Garman As costs have come down and the power of embedded platforms has increased, the hacker/maker community is playing an increasingly critical role in the creation of disruptive technologies. The "Next Big Thing" will likely start out as a hacker project using a commodity embedded hardware platform. Intel's Atom-based offerings continue to grow while targeting new niches in embedded applications. This talk will outline exciting new developments with Atom processors in the embedded space, and how hackers can make best use of these advantages. This talk will be relevant to hackers, hobbyists, and people interested in developing embedded products based on Atom, and is open to all technical experience levels.

Embedded Linux Conference 2013 - Anatomy of an Embedded KMS Driver
Sep 2, 2025
February 20, 2013 San Francisco, California The Linux Foundation Embedded Linux Conference 2013 Anatomy of an Embedded KMS Driver By Laurent Pinchart Frame Buffer Device (FBDEV) has been the dominating embedded Linux display API for more than a decade. The tide is turning and Kernel Mode Setting (KMS) is now challenging that dominant position with major embedded vendors adopting KMS as their display API of choice. Don't be left behind and discover in this talk all about KMS for embedded systems. We will go through the KMS API and learn how to write a KMS driver based on examples from a real embedded system. This talk addresses kernel developers who want to board the KMS train before it leaves. The API presentation will not require advanced development skills, but basic kernel development knowledge is recommended to understand the KMS driver internals.